HCG for Ectopic Pregnancy – The statistics on ectopic pregnancies in the United States, provided by the CDC, claim the rates of 1 in 50. Comparing the current figures with those of the past century, they’ve grown significantly. However, this has nothing to do with the frequency of pregnancies found outside the uterus. Such a difference is explained by an improved diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy.
The timely diagnosis and management of ectopic pregnancy allow for preventing severe consequences of this condition and save the mother’s health. Due to the improvement of these techniques, healthcare specialists managed to significantly reduce the maternal death rate. While reaching 10 – 15% in 1992, it has reduced to 2.7%, relying on the data provided in the Obstet. Gynecol. journal.
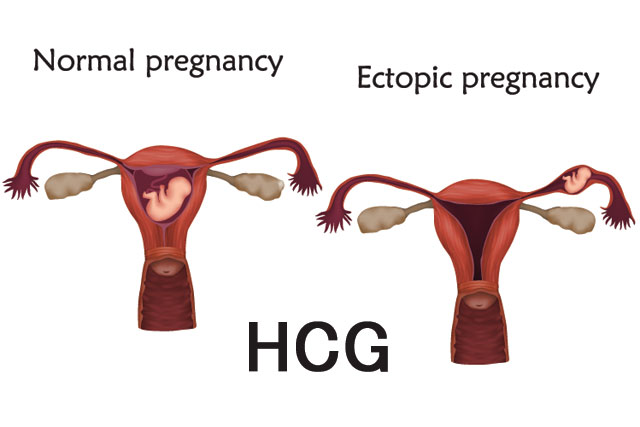
One of the most demonstrative markers of pregnancy developing outside the uterus is HCG levels. But before we get down to explaining this, let’s have a closer look at what ectopic pregnancy actually is.
What Is Ectopic Pregnancy? Its Types
Any pregnancy that develops outside the uterus is regarded as an ectopic pregnancy. In about 50% of cases, there’s no obvious reason for such an abnormality. Another half of women facing this problem may have some risk factors increasing their chances for pregnancy outside the uterus. We’ll mention some of them below:
- age older than 35;
- previous tubal or pelvic surgery;
- pelvic inflammatory disease;
- IVF and the application of other infertility treatments;
- a history of ectopic pregnancy;
- endometriosis, and others.
Depending on the place of attachment of the ectopic pregnancy, it is subdivided into several types.
- Tubal pregnancy is considered the most common, with 95% of all cases falling on it.
- Pregnancy in the cornua of the uterus happens in 2.5% of ectopic pregnancies.
- Ovarian pregnancy is diagnosed when the fertilized ovum is found in the ovary.
- Cervical pregnancy happens in less than 1% of cases and is related to the implantation of pregnancy in the cervical canal lining.
- Abdominal pregnancy is an extremely rare condition with life-threatening consequences.
Methods of Diagnosing Ectopic Pregnancy
To prove the suspected ectopic pregnancy, obstetrics and gynecology specialists carry out a complex of tests aimed at detecting the location of the gestational sack.
Transvaginal ultrasound is one of the most reliable methods of diagnosing a tubal ectopic pregnancy, as it allows for detecting the fetal pole location fast and accurately. However, sometimes, this method may fail to find the gestational sack. In such a case, it is referred to as unlocated pregnancy.
Testing for serum human chorionic gonadotropin levels is the second most informative method of diagnosing a pregnancy that develops outside the uterine cavity. Typically, HCG is checked in progress to determine its normal or abnormal increase.
In the flow of a vial intrauterine pregnancy, its levels should grow by more than 35% every 48 hours. The minimum growth rate of HCG levels for a normal pregnancy with the initial rate of 1500 mIU/mL is 49% within two days. If the initial levels range from 1500mIU/mL to 3000 mIU/mL, the HCG should grow by 40%. In patients with the starting HCG levels reaching 3000 mIU/mL, it’s 35%.
A vivid sign of an ectopic pregnancy is the enhancement in the HCG levels by less than 35% within the 48-hour range. If the figures getting on the plateau and go down, they signal about failed pregnancy.
Why do we refer to 1500 mIU/mL as a starting point? This is the so-called HCG discriminatory zone – the time point when a gestational sack can already be detected in the uterus.
As for ruptured ectopic pregnancy, it may be diagnosedby means of not only laboratory testing or ultrasound but also by visible symptoms. They include vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain. Patients with a known pregnancy and the mentioned symptoms require emergency medical help as this condition is life-threatening.
Treatment Options
The management of ectopic pregnancy depends on whether it is ruptured or not. In the first case, there’s only one way out – surgery. The operation involves a cut into the abdominal cavity to stop the hemorrhage. Usually, the ruptured fallopian tube also needs to be removed.
The options for the treatment of ectopic pregnancy that is unruptured are more diverse. One of them is laparoscopic surgery, which allows removing the pregnancy while preserving the tube. Patients whose HCG levels go down can be offered expectant management tactics, aka self-abortion of pregnancy.
Methotrexate treatment is another option available for women with ectopic pregnancy. This preparation is commonly used for medical abortion but tends to be effective for interrupting extra-uterine pregnancies as well. The success rate of a single dose Methotrexate intake reaches 69.75%. Although there is a chance that it won’t work, this method of treatment for ectopic pregnancy is preferred.
The Pros and Cons of Methotrexate for Ectopic Pregnancy
Conservative methods of treatment are always preferred over surgical. First of all, it’s due to the lower risks of bleeding and infection. Besides, such a way of resolving ectopic pregnancy is less traumatizing and stressful for a patient. Finally, based on the results of the population-based study published in the FertilSteril journal, conservative strategies allow for higher rates of intrauterine pregnancies in the 2-year perspective. 76% of women inpost-conservative treatment manage to get a healthy pregnancy within 24 months. At the same time, the rates for those treated with surgical methods don’t exceed 67%.
On the other hand, about a quarter of women following medical treatment will experience a recurrent ectopic pregnancy within 2 years. The risks for those who have undergone surgery are slightly above 18%.
It is generally considered that Methotrexate is more effective in patients whose HCG doesn’t exceed 1500 mIU/mL. Still, it is also successfully used in those with HCG reaching 3000 mIU/mL. Anyway, it’s up to you and your healthcare provider which method is better for you. The decision should be madetaking into account the entire range of factors. Evaluation of risks for recurrent ectopic pregnancy, the overall health condition of a patient, the term of gestation, the localization of the gestational sack, and others.
Final Words
Due to the progress in the methods of diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy at its early term, healthcare specialists managed to reduce the rates of mortality among pregnant women. This is a huge step forward, and HCG tests played one of the essential roles in this.
Measuring the human chorionic gonadotropin levels for detecting an ectopic pregnancy is one of the most effective methods currently used. Based on its measurements, medical specialists can choose the best treatment options for every individual patient. However, HCG cannot be evaluated separately from other tests and markers, including intravaginal ultrasound. Only working in the complex,these methods allow for effective and timely treatment of pregnancy developing outside the uterine.